
What connects Blockchain and Data Science is Data. Blockchain is a methodology that can be used to certify/validate and store data securely, whereas Data Science focuses on generating insights and predictions from data for problem-solving.
What is Blockchain?
The use of this technology came to place with cryptocurrency, where It is used to store encrypted transaction data. However, apart from storing the transaction data from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, it also has uses like storing digital data like documents, computer codes or even photos. It can also be used to manage permissions with increased security, making exploitations and data breaches impossible.
How does it work?
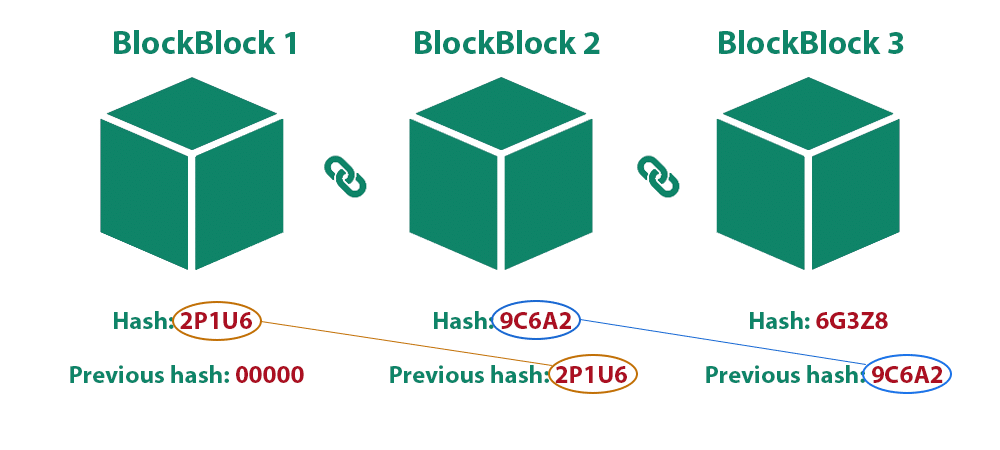
Blockchain gathers data in clustered groups known as blocks, creating a set of information. These blocks have predefined and limited storage capacity, and when one block is filled, the remaining Data is transferred to the next block, creating a linked chain. This process uses the unique signature from the previous block known as the “hash key” as the identifier and brings this identification forward in the chain, maintaining the consistency of the relationships of the blocks. The process also works as its secure data encoding mechanism giving cryptographic characteristics like data integrity, consistency, security and traceability.
Data related laws and regulations
The regulations such as the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) Singapore, are designed for the protection of natural persons related to the processing of their personal data and free movement/maintenance of personal data. They directly enforce how the storage, processing and use of personal data in Data related activities and Data Analytics Platforms need to be carried out.
Under these regulations, data points that are subjected to personal data like name, location data, identification number, online identifiers, or any sort of social identity, physical, genetic, mental, economic, or cultural identity of the natural person should be vehemently restricted to be accessed by any party or to be processed lawfully, fairly and transparently. It is also limited by the purpose, and the retention or storage and should be securely handled through a strong data governance framework that is compliant with the established regulations.
Challenges for the Data Scientists and Machine Learning/AI Engineers
Due to regulatory guidelines and the practices born around it the progress of Machine Learning and AI development has been influenced. As such;
- How to make the Data protected but still make sure they are accessible when lawful disclosure is required?
- Mechanism to share and process data to retract information relevant for insight generation/machine learning while preserving privacy.
- Getting used to working with limited data, when it is regulated by law.
- Implementation of future-proofing methods and technologies to maintain the flexibility to interpret the process of transparency.
- Maintaining compliance with multiple regional compliance regulations related to data privacy and security.
Some commonly practiced methods to maintain the aforementioned regulatory guidelines while overcoming the challenges are data pseudonymization, generalization, anonymization, synthetic data generation and encryption. Blockchain, with its unique protocols, ensures data privacy while allowing data analysts and scientists to use the Data while maintaining all the characteristics of current practices with much less effort and higher efficiency.
5 ways Blockchain Improves Data Science
1. Enhancement of the Data Integrity
The authenticity and the security of the Data is the trending requirement since 2020. Businesses nowadays collect data from various sources that may not be reliable and prone to inaccuracies. Data Scientists are now implementing Blockchain to ensure data validity across a chain of data and trace in a decentralized manner. In addition, with Blockchain trust is maintained when exchanging information among multiple parties.
2. Increased Data Accuracy
The Blockchain’s unique encryption method uses a number of private and public nodes in its digital log, therefore the data is perpetually cross-checked and validated between the blocks at their entry point. This is a unique interlinked data verification process that increases the accuracy of data.
3. Efficiency in Data Sharing
Blockchain allows viewing data in real-time and accessed by multiple users simultaneously. This makes the data administrative process more efficient.
4. Data Governance and Tracking
Data Analysts and Scientists are required to constantly track the data in their data sources and data lakes. What Blockchain provides is the ability to record data in a distinct block using a unique cryptographic key, allowing all the data users to ensure that the data possess the correct key from the original data author. This signifies the data is accurate, authentic and maintains quality.
5. Data Encoding
The transactions that happen in Blockchain are encrypted by default and recorded by a complex mathematical procedure. This makes the transactions are recorded as digital contracts making the data irreversible or immutable with protected encoding.
In Conclusion
In many ways, the concepts of data security, privacy and compliance practices are interchangeable against the odds of the regulations, leaks, breaches and potential damages by misuse, fraud, and theft.
The creative application process with the use of Blockchain promotes more regulation-compliant, secure, fair, and transparent data solution developments and practices. The void that challenges AI development progress can now be eliminated with the Blockchain disruption for more efficient, automated and personalized data solution developments in Data Science.
Rhino Partners
We are South East Asia's best software development and data science company providing customised solutions for fintech clients worldwide.